Explanation: Activity lifecycle of android
The application in an android goes through a cycle during its lifetime. There are various stages like creating, starting, resuming, pausing, stopping and destroying. The application has to undergo almost all stages. While writing the code a method is needed for calling these stages. The method will be explained further. The lifecycle can be clarified in a much better way from this figure.
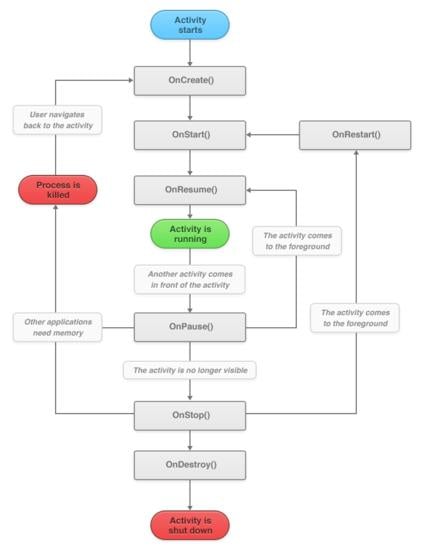
Now all these steps will be explained one by one.
Creating: This method is used when we are creating the application. The code will be like this.
[code lang=”java”]
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
[/code]
Here public specifies that this class is accessible to all subclasses. onCreate is the method used for this. Bundle is the parameter which is used for storage and we can give any name to this parameter and by default the name given to it is savedInstanceState to it. But we can give it any name but we will have to change it everywhere then like in the second step of this code.
When calling these methods we have to call the super class also which contains all the subclasses and this is done in the second line of code. setContentView tells us about the layout of the screen.
Starting: This method is called when the application is started but this method is used for a very small time because suddenly after this another method called resume is called which is explained next. The coding for this method is as follows:
[code lang=”java”]
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
TextView text = new TextView(this);
text.setText("Hello World, Android – Test");
setContentView(text);
}
[/code]
Now it is seen that what happens on the starting of the app. In this code first of all the keyword protected is used which means this method is accessible to its main class only but not to its subclasses and the keyword onStart is used to call this method. Then the TextView with the name “text” is created. The keyword new is used for dynamic memory allocation for the textview. In the next line of code it is given that what the TextView will contain. When we start the app the message “Hello World, Android – Test” appears on the screen but the time is so less that it may not be visible to us.
Resuming: This is the method which is immediately called after the onStart() method. This method is also called when the app is once paused and then started again. This method is really important in multitasking phones. Like if we are playing a game and we pause it then the task of starting it from the point where we left it is accomplished by this method. In this method the data must not be lost and hence it consumes more memory. This is the reason that when we have more apps opened in the background than the phone consumes a lot of battery and there is a time when no more apps can be run on the phone because of lots of apps in the background and phone hangs at that time.
The code for this is as given below:
[code lang=”java”]
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
TextView text = new TextView(this);
text.setText("Hello World is resumed");
setContentView(text);
}
[/code]
The code is same as in the methods explained below except the keyword onResume which is used for the resuming stage of the lifecycle. From the code it is clear that when we resume the app “Hello World is resumed” is displayed on the screen.
Pausing: This method is called when we have the app in the foreground and its not working. That means the data has to be retained but the app will not be in the running state. The code for this is almost the same except the keyword onPause. And the method stop is called soon after this method. The code is as follows:
[code lang=”java”]
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
TextView text = new TextView(this);
text.setText("Hello World is paused");
setContentView(text);
}
[/code]
Stopping: This is the method which is called when we are closing the app. It is called soon after the pausing method. The code will be like this:
[code lang=”java”]
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
}
[/code]
Summary: Till the last class we did all the coding in the .java file and all methods are called in this file only. This file is found in the src directory and in the package inside it.


