Cloud Computing Introduction
Cloud computing is defined as the delivery of computing services such as storage, servers, networking, software, databases, analytics, and artificial intelligence—via the Internet (or “the cloud”) to offer flexible resources, faster innovation, along with economies of scale. One only pays for the cloud services which they use, leading to lower operating costs, infrastructure running efficiently and easy scalability as the business needs change.
Benefits of cloud computing
Cloud computing is a major shift from the traditional functioning of the businesses, viewing the IT resources. Some of the major reasons organizations are turning to the avenue of cloud computing service are as follows:
1. Efficiency
Most of the cloud computing services are provided by self-service as well as on-demand. Thus even the huge quantity of computing resources can be easily provisioned within just a few minutes, with a few mouse clicks, providing the businesses with a lot of flexibility and taking away from the pressure of capacity planning.
2. Eliminates capital expense
Cloud computing helps to eliminate the capital expenditure of buying the hardware and software for setting up and running the on-site data centers such as the racks of the servers, round-the-clock electric supply for power generation and cooling, along with the salaries of the IT experts to manage the infrastructure.
3. Global scale
The advantages of cloud computing services involve the ability to scale elastically. As per cloud speak, this means delivering the right quantity of IT resources—for example, computing power, bandwidth, storage, —just when it is needed and from the best geographic location.
4. Performance
The biggest and most efficient cloud computing service runs on the worldwide network of the secure data centers, that are regularly upgraded for the latest generation of the fast and efficient computing hardware. It offers a large number of benefits over the single corporate data center, such as reduced network latency for the applications and better economies of scale.
5. Productivity
The on-site datacenters generally need a great deal of “racking and stacking”—hardware, software patching, along with several other time-consuming IT management activities. Cloud computing eliminates the need for a large number of these tasks so that the IT teams can spend more time on achieving the more important business objectives.
6. Security
A good number of cloud providers provide a broad set of technologies, policies, and controls that strengthen the overall security posture, aid in data protection, apps along with the infrastructure from any potential threat.
7. Reliability
Cloud computing enables data backup, disaster recovery as well as business continuity easier and cost-effective because the data can be easily mirrored at several redundant sites at the cloud provider’s network.
Types of cloud computing
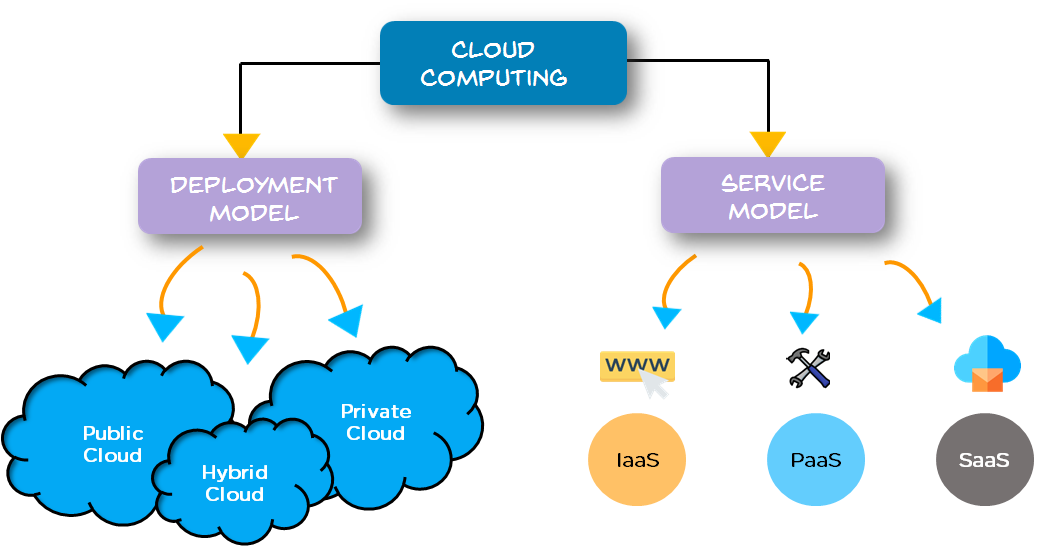
Not all of the clouds are the same and not a single type of cloud computing is suitable for every business out there. A variety of different models, types, as well as services, have evolved to help to offer the right solution for the different needs of the customers.
For this, first, one needs to determine the kind of cloud deployment or the cloud computing architecture, which the cloud services would be implemented on. There exist mainly three different methods of deployment of cloud services. These are explained as follows:
• Public cloud
The Public clouds are said to be owned and operated by the third-party cloud service providers, who deliver their computing resources such as servers and storage on the Internet. Microsoft Azure is one such example of a public cloud. On a public cloud, all of the hardware, the software and the other supporting infrastructure is managed and owned by the cloud providers themselves. One has to access these services and manage one’s account by using a web browser.
• Private cloud
The private cloud refers to the cloud computing resources that are used exclusively by only a single business or organization. The private cloud may be physically located in the company’s on-site datacenter. Some of the organizations even pay the third-party service providers for hosting their private cloud. The private cloud is said to be the one where the services and the infrastructure are maintained over a private network.
• Hybrid cloud
The Hybrid clouds combine the public cloud and the private clouds, bound together with the help of technology which allows the data and the applications to be shared amongst them. By allowing the data and applications to transfer between the private and the public clouds, a hybrid cloud provides the business with greater flexibility, better deployment options and helps optimize the existing security, infrastructure, and compliance.
Uses of cloud computing
An individual is probably using the cloud computing service right now, even if they don’t realize it. If a person uses an online service for sending an email, editing documents, watching movies or TV, listening to music, playing games or storing pictures and other files, it is most likely that cloud computing is making it all possible operating behind the scenes.
The very first cloud computing services are only a decade old, but a variety of organizations ranging from small startups to leading corporations, government organizations to non-profit agencies, all are embracing the technology for different types of objectives. Below mentioned are a few instances of what is possible today with the help of cloud services provided by a cloud provider:
• Test and develop applications
Reduce the application development cost as well as the time by making use of the cloud infrastructures which can be easily scaled up or down.
• Developing new applications and services
Efficiently build, deploy and scale a variety of applications that run on the web, mobile and API and functions on any platform. Access the resources that are needed to help meet the security, performance, and compliance requirements.
• Analyze data
Unify the data across various teams, different divisions and multiple locations on the cloud. Then use the cloud services, namely machine learning or artificial intelligence, to uncover the insights for a more informed decision.
• Back up Store, and recover data
Protect the data in a cost-efficient way —and on a large scale—by transferring the data to the Internet at an offsite cloud storage system which is accessible from any location or any device.
• Provide software on demand
Popularly known as the software as a service (SaaS), the on-demand software allows one to offer the latest version of the software updates to the customers at the time they need it, no matter where they are.
• Stream live audio and video
Connect to the audience of the business from anywhere, at any time, or on any device with high-definition audio and video having global distribution.
Market share of cloud computing
While talking about public cloud services market share, the Microsoft Azure is presently bridging the gap vs. the Amazon Web Services (AWS), whereas Google Cloud Platform ‘s (CSP) share in the market mostly remains flat, as per the report of Rightscale’s State of the Cloud. AWS and Google Cloud both continue to be the most used services pertaining to the cloud but it is also important to know which one you should use according to your needs.
Also, Google Cloud, AWS and Azure have their own set of benefits and features.
This report had been released in February 2019. It reveals several interesting facts about the cloud market updates. Almost, 94 percent of the respondents now leverage cloud technologies. The public cloud adoption is stated to be 91 percent and the private cloud adoption is rated to be 72 percent, as per Rightscale.
• Microsoft Azure has started to gain ground on the trending Amazon Web Services, especially among organizations.
• Adoption Statistics of Azure vs. AWS vs. Google Cloud:
Azure adoption grew from the earlier 45% to the present 52 %, as per the researchers.
• Google Cloud has been able to maintain its third-place, growing slightly from 18 % to 19 % adoption.
• Currently, Azure’s adoption rate is at 85 % whereas that of AWS’ is at 70 % as compared to the previous year.
• In the second year of its availability, the VMware Cloud on the AWS has achieved fourth place, increasing to 12 % adoption in 2018 as compared to 8 percent in 2017.
In order to learn more about AWS as a beginner, try out the “Learn Cloud Computing With AWS From Scratch” course. It comes with over 3 hours of video and has covered 8 important sections. These sections include topics such as introduction to AWS, set up of the SDK, AWS infrastructure, AWS Platform, and much more.
Or, you can also try the equally impressive “AWS Fundamentals for Beginners” course. It comprises of 7 hours of video and covers 6 major sections. These include Introduction to AWS, Creating an AWS Account, IAM Policies + a Quick Lab, Lab : Launching an EC2 Instance and much more.
Other key statistics amongst public cloud providers include:
• IBM Cloud rose from 15 % to 18 % which reflects a 20 percent rate of growth.
• Oracle increased its share from 10% to 16% which is a 60 percent rate of growth.
• Alibaba grew from the earlier 2% to 4% which is a remarkable 100 percent growth rate.
• China-based Alibaba Cloud also tends to have a strong adoption in the Asian market. The company is developing its footing in the European market and also supports U.S.-based companies all over the world.
Other Data Points and Findings
• The organization’s cloud expenditure is significant and is growing rapidly. Organizations plan to spend almost 24 percent more on the public cloud in 2019 as compared to 2018. Meanwhile, almost 8 % of the companies spend more than $12 million every year on the public cloud, while 50 % spend almost $1.2 million every year.
• Organizations create cloud “centers of excellence” to focus on the aspects of cloud governance. The majority of the enterprises already possess a central cloud team or a center of excellence.
• The cloud users are not doing all they can, to optimize their costs. Despite most of the respondents listing this problem as a priority, the cloud users underestimate their amount of wasted cloud expenditure. Organizations estimate almost 27 percent of waste in the year 2019.
• Hybrid cloud strategies are continually developing. Organizations that combines the public and the private clouds grew to almost 58 percent in the year 2019 as compared to 51 percent in the year 2018.
• Managing the software licenses in the public cloud is a priority for the organizations. Understanding the cost implications of the licensed software operating in the cloud is also an important challenge. Other challenges are understanding the complexity of the license rules in the public cloud as well as ensuring that they are abiding by the rules.
• Organizations run a majority of their workloads in the cloud. Organizations presently run 38 percent of their total workloads in the public cloud and 41 percent in the private cloud.
• Organizations leverage almost five clouds. Organizations are presently running the applications by way of a combination of 3:4 publics: private clouds as well as experimenting with 1.5 further for a total of 4.9 clouds. Among the organizations using a public cloud, companies are presently using 2.0 public clouds and even experimenting with 1.8 more. From those using a private cloud, organizations are presently using 2.7 private clouds and also experimenting with 2.0 more.
The Future Of Cloud Computing

Organizations these days are making maximum use of the available technology and exploring it for further to get more out of it. With cloud computing as well as the technology behind it, there exist several potential opportunities as well as capabilities. The technology of cloud computing can open up a whole new world of opportunities such as new jobs, applications, platforms, services and much more. There are a plethora of possibilities starting to surface as the future of cloud computing begins to take off. There are immense possibilities regarding Cloud services in the future.
For example, vendors, as well as service providers, can easily get on board to develop new and different techniques of selling their goods and services to their cloud users by using cloud technology. This opens up a new platform for designers and web developers. Companies can organize themselves to conduct business in a much more affordable and professional manner. The all-time popular task of social networking which helps for keeping in touch with distant family members and friends gets a new deal easier as well.
Conclusion
Thus it can be seen that the future of cloud computing is filled with unlimited possibilities and there lies a huge potential for growth. It is up to the Cloud Technology experts to make the most of what is available and exploit the area of cloud computing for better prospects when it comes to leveraging various business scenarios via cloud computing.



