Java is an incredibly diverse programming language that gives users a very rich development environment to work with. Despite the fact that it’s a very lightweight programming language, Java still has some impressive capabilities in a lot of places, not the least of which is its robust strength and adaptability to many different types of scripting challenges and unique use cases.
In this article, we’re going to discuss how you can use Java’s capabilities in order to add date and time functionality to your website or project. There are quite a few ways that this can be accomplished and the time and date function can take many different forms, as well. In this article, we’ll discuss the basic process for accomplishing the addition of time and date using Java, and we’ll also go into some detail about what each variety of time and date structure is like, and how each of them can be used most effectively.
Date constructors
The Date class is provided by Java’s basic structure. This comes from the java.util package and it’s the basic function for assessing the current time and date for an item. There are two constructors associated with dates, which are Date() and Date(long millisec). The first, Date() is the most basic constructor available. It initializes the object it’s attached to with the current date and time, according to the object’s physical location. The second, Date(long millisec) is a slightly more advanced version which counts the number of milliseconds that have occurred since midnight on January 1, 1970.
Methods
There are an awful lot of methods available for the Date class. They are, in order, boolean after(Date date), booleans before(Date date), Object clone(), int compareTo(Date date), int compareTo(Object obj), boolean equals(Object date), long getTime(), int hashCode(), void setTime(long time), String toString(). Most of these are fairly self-explanatory. Boolean operators are, of course, AND, OR, NOT. The int command works with integers, and the long command refers to the number of milliseconds that have elapsed since January 1, 1970. There are also quite a few of these commands which compare certain dates, either to the amount of time that’s elapsed since January 1, 1970, or to another arbitrary measure of time that has elapsed.
Fetching current time and date
This is quite a simple process. The simple Date object with the command toString() can be used to print the date that is current to the item that the method is engaged with. Importing the utility from java.util is the part of the process that attaches the date to the method that is printed by the process.
Ways to compare dates
In general, there are three ways to compare two dates using Java. The first is to use getTime(), which compares the number of milliseconds that have elapsed since January 1, 1970 for each of the two objects, and then compares them. The second method is to use the before() after() and equals() commands to create a sort of situation where the different dates are automatically compared by virtue of their separate commands which will return the compared date after the mathematics are worked out automatically. The third and final method is the most direct – you can use the compareTo() method, which requires a specifically filled out data interface which is then automatically implemented in the return for the object, which then displays the date.
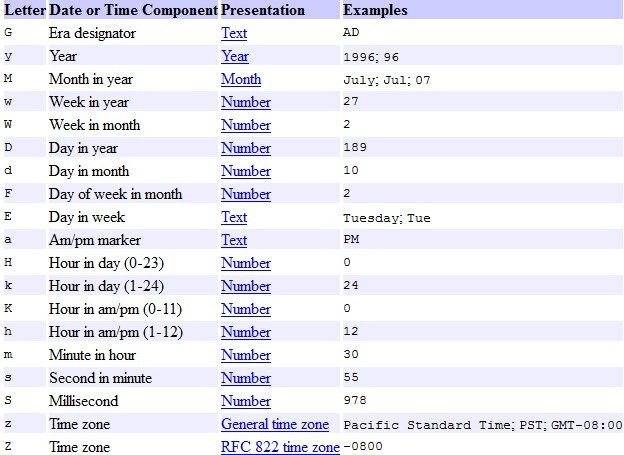
There are a ton of different simple formatting codes for dates. All of these are ASCII codes, so familiarity with that is a plus. In general, they correspond a letter to a description code. Usually, these are quite intuitive. For example, M stands for Month in year, which could return as either July or 07. The same is true for d which stands for Day in month, which returns as a numerical value such as 10. Some of these aren’t as intuitive, such as G, which signifies an era, such as AD or BCE or a which stands for A.M./P.M..
Conversion characters
Conversion characters are really similar to the formatting dates. These, however, aren’t as intuitive or quick to grasp as the formatting ones because they’re more specifically keyed to things like digits and week formatting. Again, there are too many to list, but there are a few examples of how these work. B, for example, is a full month name, like May or July. Meanwhile, b is an abbreviated month name, like Jul or Feb.
Sleeping
You can use a time function to set a timer so that a program will sleep for an amount of time that you specify.
Measure time that has elapsed
You can command computers to sleep for a while, and use a function to count the milliseconds from when it goes to sleep to when it wakes up again to preserve the time function. This time can also be used as a timer for other things.
Gregorian calendar
Part of the basic Java calendar class is a hard-coded Gregorian calendar. This means that you can implement time and date functions based on the calendar that you’re familiar with. This gives you access to a ton of different commands, such as constructing calendars based on Gregorian months and syncing things together based on the current Gregorian time.
The Java 8 date and time API is a pretty complex feature that could, honestly, take its own article to explain. However, the important thing to remember about it is that it’s an expanded form of the Java things from earlier versions. This means that it has expanded class material and it can function with a more precise internal clock than earlier versions.
There’s a lot to consider when it comes to time and date in Java, but in general, these are the things that you’ll need to know about if you’re considering using the date and time features in Java’s library.