![Red-Hat-Linux-Administration---(9)-The-vim-Editor-[2-of-2]-740X296](https://blog.eduonix.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Red-Hat-Linux-Administration-9-The-vim-Editor-2-of-2-740X296.jpg)
In this article, we will complete the topic we started in the previous article: the vim Editor.
The Ex Mode
From the Command mode, type : to start the Ex mode. When you do, a colon : appears in the lower left corner of the vim screen.

After the colon, you can type a short command and execute it by pressing Enter. The common operations you could execute from this mode are:
:n transfers the cursor to line number n.
:w writes (saves) the current file to disk.
:wq saves changes to disk and exits.
:q! discards any changes made in the file and exits to shell.
:q exits the vim editor.
Example
In this example, we want to create a new file test01, and fill it with some data.
To do this, follow these steps:
- In your shell, type vim test01
- In the vim screen, press i (or Insert or I) to start the Insert mode.
- Write some lines as below.

- To save the file, press Esc to return to the Command mode.
- From the Command mode, type :wq and press Enter.

Now, you could verify what you have written by displaying the contents of the created file:

The Command Mode
This is the default mode you get when starting the vim editor. In this mode you could:
- Move the cursor around the file: left and right, up and down.
- Search for a pattern.
- Replace text.
- Delete (cut) text.
- Copy text.
- Paste copied or cut text.
- Undoing changes.
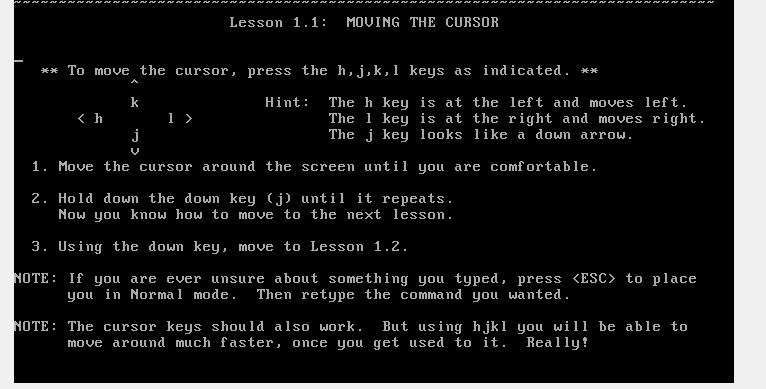
Moving the Cursor
- You can move the cursor using either the arrows: left, right, up and down keys, or using the letters h,l, k, and j, respectively.
- To jump to the end of the file, use G (Shift + G)
- To jump to the first line, press 1G.
- To move to the next word: press w.
- To move back to the previous word: press b.
- To move to the beginning of the line, press 0.
- To move to the end of the line, press $.
Searching for a Pattern
To search for a substring in the vim editor, press / in the Command mode, and type the text to search for, then press Enter. The matched text is highlighted.

To move to the next match, press n. To go back to the previous match, press N.
Deleting Text Character by Character
Pressing x in the Command mode deletes the character at the cursor position.
Replacing Single Character
To replace a single character, move the cursor to the character you need to replace, and press r. Now type the new character to replace the original.
Replacing Multiple Characters
Press R to start replacing characters starting from the current cursor position. To stop replacing characters, press Esc.
Copying Text
- To copy a word, press yw.
- To copy two words press y2w.
- To copy n words, press ynw.
- To copy the current line, press yy.
- To copy n lines, press yny.
Deleting (Cutting) Text
- To delete a word, press dw.
- To delete n words, press dnw.
- To delete the current line, press dd.
- To delete n lines (starting from the current line), press dnd.
Pasting Text
- To paste text before the cursor, Press P.
- To paste text after the cursor, Press p.
Undoing Changes
- To undo the last change, press u.
- To undo all changes made to the current line, press U.
Redo Undone Changes
To redo the last undone modification, press Ctrl + r.
The vim Tutorial vimtutor
Learning vi/vim is not an easy task. You may suffer in the beginning (for a month or two), until you become familiar with vim. To help you in this task, the vim installation package includes a tutorial named vimtutor.
![]()
The tutorial consists of a series of lessons that teaches you the ABCs of vim, upto the mastering level.
Summary
That was part two of the topic discussing the vim Editor.
- From the Ex mode, you could save, discard changes, and quit the editor.
- From the Command mode, you could move cursor, delete characters, delete words and lines, copy words and lines, paste copies or cut text, search for a pattern, replace single or multiple characters, and undo/redo changes.
- The command vim FILENAME opens the vim editor for creating the file (if it doesn’t exist), or for editing it (if it already exists).
- The vim installation package includes a useful tutorial vimtutor.
I hope you find this article useful. See you in the next article.


