With so many security breaches & scams happening every single day, the concept of smart contracts can turn out to be the messiah of this digital world! To know more about this technology, here’s an exclusive article giving insights into the smart contract, how smart contract works & its importance!!
Decoding Smart Contracts!!
The smart contract is defined as an agreement that takes place between two people by way of computer code. The contract runs on the blockchain, and hence they are stored on a public database that cannot be altered.
The transactions which take place in a smart contract can be sent automatically without any interference from the third party. This indicates that there is no individual to rely on to validate the transaction. The transactions only take place when the conditions of the agreement have been met — there is no third party, so there are no issues with trust.
Also Read: Everything You Need To Know About Blockchain In 7 Mins!!
Origin of smart contract!
In the year 1994, Nick Szabo, who was a cryptographer, came out with an idea of making it possible to record several contracts in the form of computer code. Such a contract would be activated by itself when certain terms and conditions have been satisfied. The idea has the potential to eliminate the need for a trusted third-party organization (such as a bank).
But why?
The answer to this is easy — because an individual is no longer in need of a trusted third party at the time of making a transaction. Rather, the contracts (or the transactions) are self-executed through a trusted network that is completely under the control of computers.
The creator, Szabo had worked on this idea for several years and has written a book titled “Smart Contracts: Building Blocks for Digital Free Markets”. The issue with the system was that back then in 1994, blockchain technology was not popular as of now.
In the year 2009, Bitcoin introduced the primary use of blockchain technology. Next during the year 2015, Ethereum had been founded by an intellectual young chap named Vitalik Buterin, and this is where the first working smart contracts came into existence. The Smart contracts are self-executing, business automation applications that operate through a decentralized network such as a blockchain.
Since these transactions are done via smart contact, these can eliminate the administrative overhead. Due to this reason, smart contracts are considered to be one of the most endearing features associated with Blockchain technology.
While the blockchain technology acts as a form of database, ensuring that the transactions have been implemented, the smart contracts execute the pre-determined conditions; similar to the computer executing the “if/then,” or conditional, programming.
Primarily, once some of the essential conditions of a smart contract are met, such as goods arriving in a port, two parties accept to exchange in cryptocurrency – then they can automate the transfer of the bitcoin, fiat money, or the acceptance of a shipment of goods which allows them to go ahead on their journey.
Also Read: Why 2020 Is the Year of Decentralized Exchange (Dex)?
Understanding tokens & smart contracts
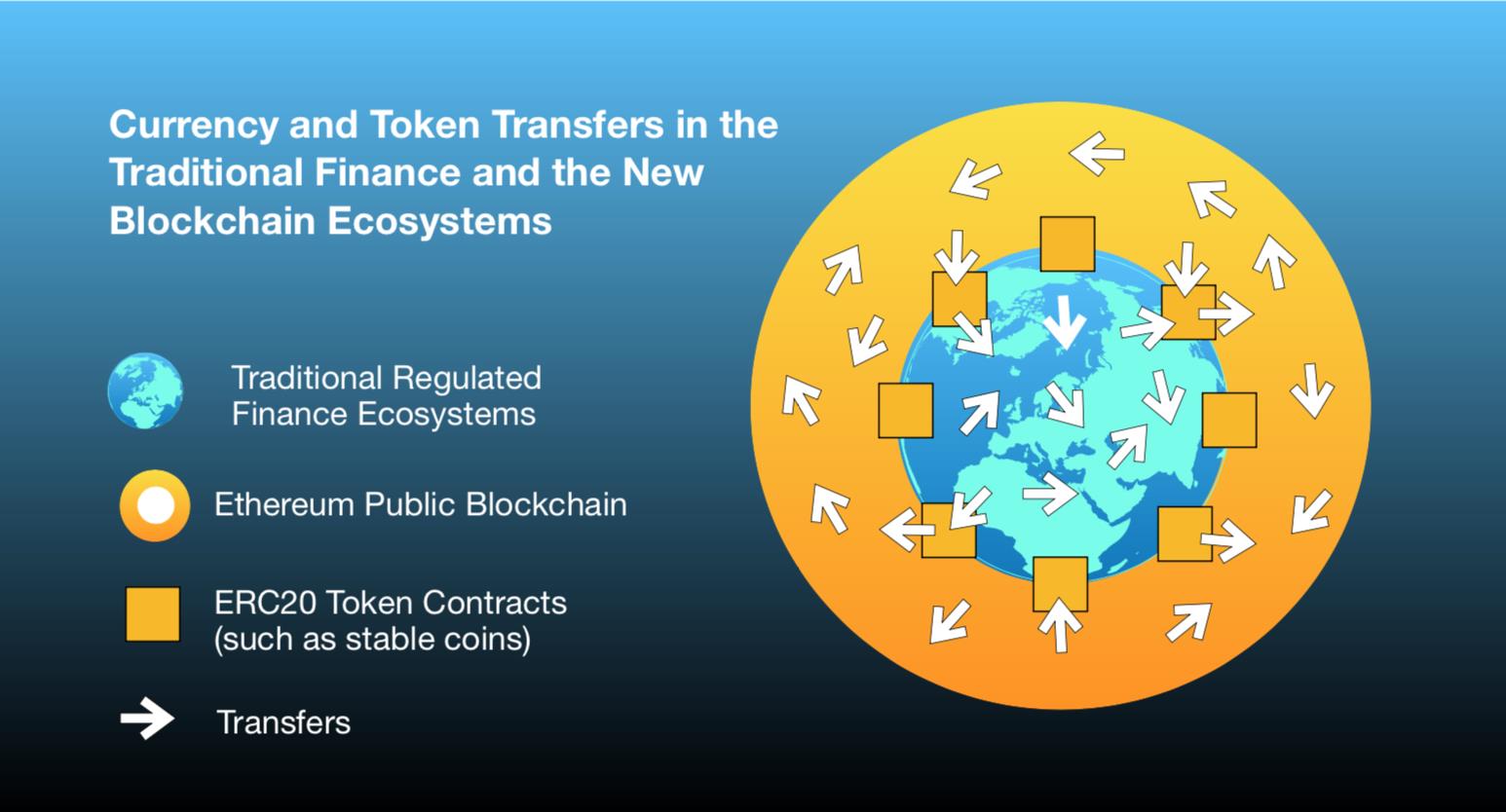
For instance, an insurance company may use smart contracts to automate the release of claim money depending upon the events like large-scale hurricanes, floods, or droughts. Or, once the cargo ship reaches the port of entry and the IoT sensors inside the container ascertain the contents are new and remained stored properly all through the journey, a bill of lading can be automatically issued.
Smart contracts are even considered to be the basis of the transference of the cryptocurrency and the digital tokens (in other words, a digital representation of the physical asset or utility). Smart contracts can regulate the transfer of other cryptocurrencies, such as bitcoin.
After the payment has been verified, the bitcoin is allowed to change hands from the seller to the buyer. Most of the enterprise blockchain networks do not use the token. But in the ones which do, the rules in the smart contracts govern how the tokens get allocated along with the conditions of transfer.
Also Read: Zero-Knowledge Proof- There won’t be any information to hack!
How smart contracts can mimic business rules?

The Smart contracts are neither “smart” nor are the contracts in the legal sense. They are just business rules converted into software. People generally ask what makes the smart contracts stand apart from the normal business rules automation software or stored procedures.
The answer to this is that technically, the principle is the same; but the smart contracts can support the automating processes which stretch across the corporate boundaries, including multiple organizations. In other words, because smart contract code is running atop an open blockchain ledger, rules can be applied not only within the corporation that coded the smart contract but to other business partners permitted to be on the blockchain.
In other words, they’re code that does what it’s been programmed to do. If the business rules have been defined badly and/or the programmer doesn’t do a good job, the result is going to be a mess.
And, even if designed and programmed correctly, a smart contract isn’t smart – it just functions as designed.
Modum SAP blockchain IoT
Translating business rules into code doesn’t automatically turn the result into a legally enforceable agreement between the parties involved (which is what a contract is). Although there are some initiatives aimed at making smart contracts automatically legally binding, that path – at least for now – fraught with difficulty and risk, Bennett said. That’s because there’s no agreed standard definition of what a smart contract is?
Edge computing, IoT and the future of smart contracts
Over the next several years, the massive growth in IoT connected devices could spur greater use of smart contracts. That’s because a substantial portion of the estimated 46 billion industrial and enterprise devices connected in 2023 will rely on edge computing.
As a result, addressing standardization and deployment issues will be crucial. Smart contracts could offer a standardized method for accelerating data exchange and enabling processes between IoT devices by removing the middleman: the server or cloud service that acts as the central communication spoke for requests and other traffic among IoT devices on a network.

Fundamentally, the idea is you don’t have a central agent – no one approving and validating every single transaction. Instead, you have distributed nodes that participate in invalidating every transaction in the network.
Blockchain ledgers decrease the time required to complete IoT device information exchange and processing time. It could be in an automotive manufacturing plant. As soon as a certain part arrives, that part then communicates that to other nodes at that destination, which would agree that part arrived and communicate that to the entire network. The new node would then be allowed to begin its work.
The rise of edge computing is critical in scaling up tech deployments, owing to reduced bandwidth requirements, faster application response times, and improvements in data security.
While financial services and insurance companies are currently at the forefront of blockchain development and deployment, transportation, government, and utility sectors are now engaging more, due to the heavy focus on process efficiency, supply chain, and logistics opportunities. And that’s expected to combine to make smart contracts more ubiquitous in the years ahead.
Also Read: Blockchain Impacts Goes Beyond The Financial Services
Security – A Prime Concern

Considering the safety and security aspect of the smart contract, not all are 100% safe when it comes to transactions. A scripted smart contract is visible to all the members of the said blockchain raising the fear of bugs, malware, and illegal theft.
Some experts have claimed that the security holes are almost visible and these couldn’t be fixed in a matter of minutes if some suspicious activity happens over time. Back in the year 2016, DAO faced a similar attack.
Despite the reported incidents of bugs, malware, attacks on the blockchain network, and immutability of the bugs found in the system, there is an absence of a central or single source that could be referred to for guidelines. Keeping in view the volatile condition in the smart contract scenario, blockchain developers are working their way through creating dependable, most secure, and centralized contract systems.
Conclusion –
A smart contract is a facilitator of currency exchange on the digital blockchain platform. Despite various ups and downs, its journey has been of growth, enlargement, and hope or all people dealing in cryptocurrency.
Also Read: An Ultimate Guide to Smart Contracts!









