We’ve dealt with the issue of securing your private data on this site already. Today we’re expanding the topic to include the security of your company’s data online. Or, to be more specific, how you improve the security of your remote employee’s home networks.
Why Focus on Remote Workers?
Like it or not, remote working was on an upward trend long before COVID-19 appeared on the radar. The current crisis has forced companies to accelerate their plans to allow employees to work from home.
According to Statista, Microsoft’s seen users of their Teams app more than double since 2019. Flattening the COVID-19 curve has been very good for Microsoft. See for yourself in the chart below.
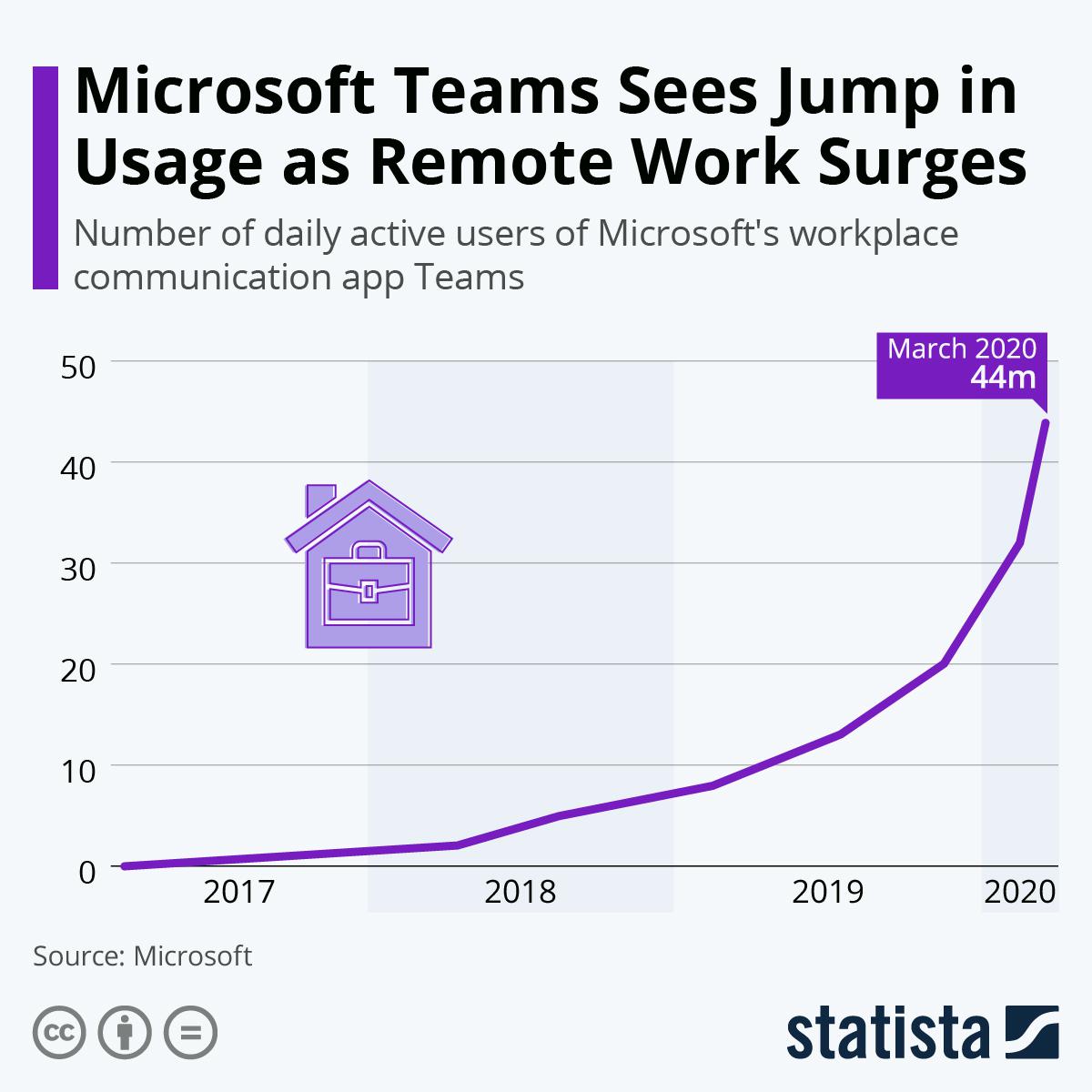
That’s great news for Microsoft, but it’s bound to leave other companies exposed. You can control the environment at your office, but an employee’s home is something different. Fortunately, there are concrete measures that you can employ to ensure that remote working poses minimal risk to your company’s data security.
Your primary weapon in this fight is to focus on an employee’s home network security. Here’s how to go about this.
Start With the Computer Itself
Great cybersecurity starts with ensuring that threats, like ransomware, are appropriately managed. Plan for the worst-case scenario, and you’re halfway there.
Before we move onto the home network security, is the data on the computer itself secure? Has it been adequately encrypted? Is the information protected by a strong password? Do you have to input a password on boot up? Does the computer sign out automatically after a period of inactivity?
Finally, make sure that the device has a good anti-virus program installed. Set the security settings as high as possible to ensure that your exposure is limited.
Why’s this important?
You don’t know who’ll have access to the computer at home. Could someone try to sneak a peak? What happens if someone steals the laptop? Securing your data on the computer is your first line of defense.
Your Remote Worker’s Home Network Security
Now let’s get to the good stuff – securing the home network itself.
It Starts With a Simple Network Scan
Many cybersecurity companies have apps that allow you to scan for network vulnerabilities. Run one of these on each employee’s home network before allowing them to connect up work computers. These apps will check what other devices link into the system, whether or not the software is up to date, and if there are weak spots.
Why’s this important?
Outdated software might mean missing out on important security updates. All software should be kept up to date to ensure the best security.
Check What Router Security They’re Using
If they’re like most people, they’ve probably stuck to the protocols set up by their internet service provider.
Check to ensure that network encryption is enabled. They must check the encryption options on the network. WPA2 is a good option that provides a high level of encryption.
Why’s this important?
Encryption makes it more difficult to intercept data sent over a Wi-Fi connection.
Change the Router’s SSID Name
Finding out how to do this may mean looking up a manual. You’ll want to make sure it’s done, though.
Why’s this important?
Hackers will use software to pick up all Wi-Fi connections in the area. Even when the router doesn’t broadcast its name, the software can pick up that there’s a connection. The SSID name tells them exactly what the router is online.
This could make it easier for them to carry out a hack.
Make Employees Set Up A Guest User On the Network
Employees should set up a separate guest user on their home networks. This is the connection that they must use when working. The rules are simple:
- They must set a secure password of at least 16 characters for the guest user.
- The password must be unique.
- No one else is to have this password.
- They can’t connect any other devices to the connection.
In your home, how many devices connect through to your Wi-Fi connection? Families might have several smartphones, a smart TV and other smart devices, printers, and so on, sharing the same link.
Why’s this important?
If you’re all using the same default Wi-Fi network, what affects one device could affect the others. So, if some hacker infects your Smart TV with malware, it could spread to all the other devices on the network. Keeping your work device separate keeps it safer.
Disable Discovery Options
Many networks allow you to see what other devices are present nearby. This is to make it easier for you to connect to a nearby printer. This is the opposite of what you need here. Ensure that your work device can’t detect or be seen by other devices using the Wi-Fi connection.
Why’s this important?
If a hacker does breach one of the other devices on the network, you don’t want them to pick up yours.
Disable Bluetooth Options as Well
Before you say that Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are two separate things, we know. We’re just adding this in there as a reminder.
Limit the Signal’s Range if Necessary
Sign onto any service provider’s network at home, and you’ll see that it picks up numerous connections. Let employees read through the manual of the router to understand how to limit the range effectively.
Why’s this important?
If you don’t limit the signal to within your home, your neighbors can detect it. That’s one of the reasons that these networks are password protected. Still, if your neighbor knows something about hacking, they might try to hijack the signal. The same can happen at the employee’s home.
Set Up a Secure VPN
For a VPN remote working plan to be efficient, you’ll need to make sure it passes protection, speed, and safety tests. Subscribe to a VPN has a “no logs” policy, so your business data is not sold to third-party merchants. Make sure the VPN has a Kill-Switch, so if your connection drops, your business intelligence won’t be exposed.
Final Notes
Will these steps stop a determined hacker? No. Will they prevent your employees from mistakenly downloading malware? No. What these steps will do, however, is to make it harder for bad actors to find and hijack your signal. This improves one aspect of security for your company and benefits your employees as well.









